The Auckland Unitary Plan is currently in notified stage, and has reached the Council Decisions stage. Essentially this means the plan is still a ‘Work In Progress’ however we are now much closer to having the Unitary Plan being operative. Until the Auckland Unitary Plan is Operative we would not recommend making purchases based on the zoning measures of what a property will be under the Plan as it could still change.
If you are making important decisions based on the Auckland Unitary Plan I recommend that you either talk to Town Planning at Auckland City Council and/or check the online version of the Plan to ensure that the the controls you are making a decision on are current and conduct your own due diligence investigation into the same. You can access the online Auckland Unitary Plan Book here.
The information in this post is from the www.shapeauckland.co.nz, www.unitaryplan.aucklandcouncil.govt.nz and www.aucklandcouncil.govt.nz website on October 13th 2013. The current version of the plan has changed in parts from the below, we are awaiting for the plan to be a fomalised version to be able to update the below. Accordingly I cannot guarantee it’s accuracy and reliability as we have not checked, audited, or reviewed the information and this may have changed from date of posting and todays date, therefore I do not accept any responsibility to any person for the accuracy of the information herein.
When you are looking at the Auckland Unitary Plan zone rules that will impact your property, it is important to check both the controls and the rules. You can see the rules for the Auckland Unitary Plan Zone Rules here.
If you are making important financial decisions based on the Auckland Unitary Plan it is highly recommended that you speak to Town Planning at Auckland City Council or a Registered Surveyor.
Below are the rules from the Unitary plan rule book for the Terraced Housing and Apartment Zone.
PART 3 – REGIONAL AND DISTRICT RULES»
Chapter I: Zone rules»1 Residential zones»
9. Development Controls – Terrace Housing and Apartment Buildings zone
The following development controls apply in the Terrace Housing and Apartment Buildings zone.
9.1 Development control infringements
- Buildings that infringe three or more of the following development controls are a discretionary activity:
- building height
- yards
- building setbacks within the Terrace Housing and Apartment Buildings zone
- building setbacks adjoining lower density zones
- maximum impervious area
- building coverage
- landscaping
- outlook.
9.2 Building height
Purpose: manage the height of buildings to provide for terrace housing and apartments of between four and six storeys.
- Buildings must not exceed 13.5m and four storeys in height or 14.5m and four storeys in height where semi-basement parking is provided. Semi-basement parking must not exceed 1m in height.
- If the site is subject to the Additional Building Height overlay, buildings must not exceed the height in metres shown for the site on the planning maps. Additionally, buildings must not exceed the corresponding height in storeys for the height in metres specified in the table below.
Table 7:
| Building height in metres | Building height in storeys |
| 20.5m | 6 storeys |
| 17.5m | 5 storeys |
9.3 Yards
Purpose: provide an attractive transition from the street to the front facade of the terrace housing or the apartment building and ensure dwellings are adequately set back from lakes, streams and the coastal edge to maintain water quality and provide protection from natural hazards.
Table 8:
| Yard | Minimum depth |
| Front | 2.5m |
| Riparian | 10m from the edge of all other permanent and intermittent streams |
| Lake | 30m |
| Coastal protection yard | 10m, or as otherwise specified inappendix 6.7 |
9.4 Building setbacks within the Terrace Housing and Apartment Buildings zone
Purpose: minimise the adverse effects of building height on neighbours (i.e. dominance and shading) and reduce the overall visual dominance of buildings at upper levels.
- Where sites in the Terrace Housing and Apartment Buildings zone adjoin another site in the same zone or any other zone not specified in clause 9.5 below, the building must be set back from side and rear boundaries as follows:
- Where the building is from one to four storeys in height the building must be setback from side and rear boundaries at least:
- 3m for storeys one and two
- 5m for storeys three and four.
- Where the building is more than four storeys the building must be setback from side and rear boundaries at least:
- 5m for storeys one to four
- 7m for storeys five and six.
- Where the building is from one to four storeys in height the building must be setback from side and rear boundaries at least:
Figure 17: Building setbacks adjoining other Terrace Housing and Apartment Buildings zone sites

Figure 17a
Figure 17b

- This control does not apply on boundaries where a common wall of the same height exists or is proposed.
9.5 Building setbacks adjoining lower density zones
Purpose: provide an appropriate transition in building bulk and scale to lower density residential zones and small public open spaces.
- Where sites in the Terraced Housing and Apartment Buildings zone adjoin sites in the Single House zone or sites less than 2000m² in the public open space zones, the building must be set back from side and rear boundaries as follows:
- 5m for storeys one and two
- 9m for storeys three and four
- 13m for storeys five and six.
Figure 18: Building setbacks adjoining Single House zone sites and sites within the public open space zones less than 2000m²

- Where sites in the Terrace Housing and Apartment Buildings zone adjoin sites in the Mixed Housing Suburban and Mixed Housing Urban zones, buildings must be setback from side and rear boundaries as follows:
- 3m for storeys one and two
- 7m for storeys three and four
- 11m for storeys five and six.
Figure 19: Building setbacks adjoining Mixed Housing Suburban and Mixed Housing Urban zone sites

- This control does not apply where a common wall of the same height exists or is proposed.
9.6 Minimum frontage and site width
Purpose: ensure sites are of a size sufficient to:
- enable higher density development including apartment buildings
- provide a positive interface with the public realm
- provide a good standard of on-site amenity.
- A site must be at least 25m wide:
- at the road boundary
- for at least 80 per cent of the length of its side boundaries
- where a building of up to four storeys is proposed.
- Where a building of more than four storeys is proposed, a site must be at least 30m wide:
- at the road boundary
- for at least 80 per cent of the length of its side boundaries.
9.7 Maximum impervious area
Purpose: manage the amount of stormwater runoff generated by a development.
- Maximum impervious area: 60 per cent.
- Maximum impervious area within a riparian yard: 10 per cent.
9.8 Building coverage
Purpose: provide for a mid-rise urban built character within the zone.
- Maximum building coverage: 40 per cent.
9.9 Landscaping
Purpose:
- provide for on-site amenity and an attractive streetscape character
- improve stormwater absorption on-site.
- At least 40 per cent of a site must comprise landscaped area.
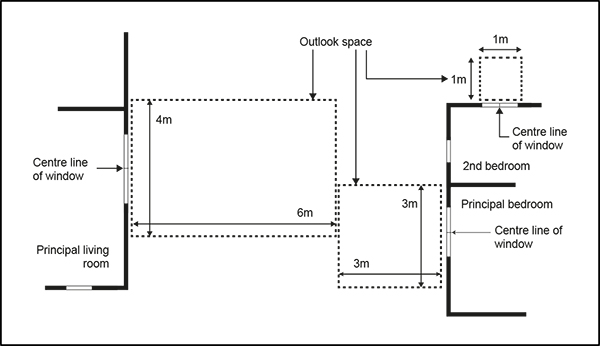
9.10 Outlook space
Purpose:
- Ensure a reasonable standard of visual and acoustic privacy between different dwellings, including their outdoor living space, on the same or adjacent sites
- Encourage the placement of habitable room windows to the site frontage or to the rear of the site in preference to side boundaries, to maximise both passive surveillance of the street and privacy, and to avoid overlooking of neighbouring sites.
- An outlook space must be provided from the face of a building containing windows or balconies to a habitable room. Where the room has two or more external faces with windows or balconies the outlook space must be provided from, in order of priority, the face with the largest balcony or largest area of glazing.
- The minimum dimensions for a required outlook space are as follows:
- principal living room: 6m in depth and 4m in width
- principal bedroom: 3m in depth and 3m in width
- all other habitable rooms: 1m in depth and 1m in width.
- The depth of the outlook space is measured at right angles to and horizontal from the window or balcony to which it applies. Where the outlook space applies to a balcony, it must be measured from the outside edge of the balcony.
- The width of the outlook space is measured from the centre point of the largest window on the building face to which it applies or from the centre point of the largest balcony.
- The height of the outlook space is the same as the floor height, measured from floor to ceiling, of the building face to which the control applies.
- Outlook spaces may be within the site, over a public street, or other public open space.
- Outlook spaces required from different rooms within the same dwelling may overlap.
- Outlook spaces must:
- be clear and unobstructed by buildings
- not extend over adjacent sites or overlap with outlook spaces required by another dwelling.
- An outlook space at ground floor level from a principal living room may be reduced to 4m deep if privacy to adjacent dwellings is provided by fencing at least 1.6m in height.
Figure 20: Required outlook space
h5>9.11 Separation between buildings within a site
Purpose: require reasonable separation between buildings on the same site to manage dominance, provide access to daylight and natural ventilation.
- Buildings must be separated where the habitable room of a dwelling has windows or balconies that face out to the wall of another building on the same site (the facing wall). Where the room has two or more external faces with windows or balconies the building separation must be applied from, in order of priority, the face with the largest balcony or the largest area of area of glazing.
- The separation space required must be free of buildings for the depth, width and height set out below.
- The depth of the separation space is measured at right angles to, and horizontal from, the window or balcony to which it applies across to the facing wall, excluding eaves or guttering. Where the building separation applies to a balcony, it is measured from the outside edge of the balcony.
- For the principal living room, the depth of the separation space required is equal to the height of the facing wall above the floor level of the habitable room, or 15m, whichever is the lesser.
- For the principal bedroom, the depth of the separation space required is 6m.
- For other habitable rooms , the depth of the separation space required is 3m.
- The width of the separation space is 50 per cent of its depth and is measured from the centre point of the largest window on the building face to which it applies or from the centre point of the largest balcony.
- The height of the separation space is from the height of the floor or balcony upwards, clear to the sky except that eaves or gutters may protrude into it.
- Where the adjacent building is not perpendicular to the distance being measured, the minimum separation depth required must be measured as an average around the centre line of the window/balcony.
9.12 Outdoor living space
Purpose: provide dwellings with outdoor living space that is of a usable size and dimension for the type of dwelling and is accessible from the principal living room.
- A dwelling with the principal living room at ground level must have an outdoor living space capable of containing a delineated area measuring at least 20m² that:
- has no dimension less than 4m
- is directly accessible from the principal living room
- has a gradient not exceeding 1 in 20.
- Where an entire dwelling is above ground level, it must have an outdoor living space in the form of a balcony or roof terrace that:
- is at least 8m²
- has a minimum depth of 2.4m.
9.13 Maximum building length
Purpose: require breaks in building facades and manage the length of buildings along side and/or rear boundaries and the separation between buildings on the same site to visually integrate them into the neighbourhood.
- There must be a recess in the façade of a building where it faces a side or rear boundary from the point at which the building exceeds a length of 16m. The recess must:
- be at least 2m, for a length of at least 4m
- be for the full height of the wall, excluding any structures 1m or less in height above ground level
- include a break in the eave line and roof line of the façade.
- The maximum length of a building along a side or rear boundary is 30m, after which there must be a separation of at least 5m along the same boundary to any other building on the same site.
9.14 Fences
Purpose: enhance passive surveillance over the street and public open space and maintain the open character of front yards.
- Fences in a front yard must not exceed 1.2m in height.
Figure 21: Fences within the front yard

9.15 Garages
Purpose:
- reduce the dominance of garages as viewed from the street
- avoid parked cars over-hanging the footpath.
- A garage door facing a street must be no greater than 40 per cent of the width of the front facade of the dwelling to which the garage relates.
- Garage doors must not project forward of the front façade of a dwelling.
- The garage door must be set back at least 5m from the site’s frontage.
9.16 Minimum dwelling size
Purpose: dwellings are a sufficient size to provide for the day-to-day needs of residents.
- Dwellings must have a minimum net internal floor area as follows.
- 40m2 for studio dwellings
- 45m2 for one bedroom dwellings.
9.17 Daylight to dwellings
Purpose: ensure dwellings receive a good degree of daylight.
- The principal living room must have external glazing that is at least 40 per cent of the floor area of that space.
- Bedrooms must have external glazing that is at least 20 per cent of the floor area of that space.
9.18 Minimum dimension of principal living rooms and principal bedrooms
Purpose: principal living rooms and bedrooms are of a size sufficient to accommodate standard size furniture and circulation space.
- The principal living room within a dwelling must have no dimension less than 3m, measured perpendicular from the internal walls of the room.
- The principal bedroom within a dwelling must be at least 3m in width and 3.5m in length measured perpendicular from the internal walls of the room. Cupboards and other storage space may be included in the minimum dimension.
9.19 Servicing and waste
Purpose: dwellings within medium to large-scale residential development have sufficient space within the building to accommodate the storage of waste.
- A building or development containing 10 or more dwellings must provide a communal storage area for waste. The size of the communal storage area must be an aggregate of the minimum areas specified for the dwelling types below:
- studio and one bedroom – 0.3m²
- two bedrooms – 0.5m²
- three bedrooms – 0.7m²
- four or more bedrooms – 1m².
- An additional 30 per cent in area of floor area required above must be provided within the communal storage area for manoeuvring or sorting within the waste storage area.
9.20 Storage
Purpose: ensure dwellings have sufficient space for the storage of everyday household items and bulky items, such as bicycles.
- A building or development containing five or more dwellings must provide covered storage space for each dwelling with internal measurements of at least 4m3, excluding storage within the kitchen and bedroom wardrobes. The storage may be within the dwelling or external to it, within the site.
- The required storage space for each dwelling must include a single covered storage space within internal dimensions of at least 2m3.
9.21 Dwelling mix
Purpose: large-scale residential development provides variety in dwelling sizes.
- In a single development containing more than 20 dwellings, the combined number of studio and one bedroom dwellings must not exceed 70 per cent of the total number of dwellings within the development.
9.22 Minimum floor to floor/ceiling height
Purpose: buildings are adaptable to a wide variety of uses over time and provided with adequate daylight access.
- The ground floor of a new building must have a minimum finished floor to floor height of 4m for a minimum depth of 10m where it adjoins an arterial road.
- In all other instances, the finished floor to finished ceiling height of habitable rooms must be at least 2.55m.
9.23 Universal access
Purpose: medium to large-scale residential development provides equal physical access and use for people of all ages and abilities.
- Where a new building or development contains 10 or more dwellings, 20 per cent of those dwellings must comply with the following:
- doorways must have a minimum clear opening width of 810mm
- stairwells must have a minimum width of 900mm
- corridors must have a minimum width of 1050mm
- the principal means of access from the frontage, or the parking space serving the dwelling, to the principal entrance of the dwelling must have:
- a minimum width of 1.2m
- a maximum slope of 1:20
- a maximum cross fall of 1:50.
- Where the calculation of the dwellings required to be universally accessible results in a fractional dwelling, any fraction that is less than one-half will be disregarded and any fraction of one-half or more will be counted as one dwelling.
- All dwellings required to be universally accessible must provide at least one parking space for people with a disability. The dimensions and accessible route requirements for such parking spaces are detailed in Section 5.5 of the New Zealand Building Code D1/AS1 New Zealand Standard for Design for Access and Mobility – Buildings and Associated Facilities (NZS 4121-2001).




[…] Click here for the key facts PDF sheet, or click here for the Terraced and Apartment zone rules in detail. […]